
Whole Genome Sequencing Program
Rapid whole genome sequencing is a state-of-the-art test that can quickly identify genetic disorders in a fetus or baby with unexplained health complications. It's the most comprehensive genetic test available.
While other genetic tests look at a small number of genes to check for a few specific conditions, whole genome sequencing analyzes the patient's entire genome (all the genes and the DNA between genes). By casting the widest net possible, we can quickly detect almost any genetic issue, including rare conditions that might otherwise go undiagnosed. Finding the underlying cause allows doctors to determine the best care for your baby from the start.
We are the only hospital in Northern California to provide this test for both fetal and newborn patients. Pregnant patients can access fetal testing at our Fetal Treatment Center, and newborn testing is available to babies in our neonatal intensive care units (NICUs).
Rapid whole genome sequencing is performed and analyzed here at UCSF, and results are available quickly – usually within two to four weeks. Getting results fast can be particularly important for conditions that need prompt treatment. For example, early intervention can dramatically change the course of inherited metabolic disorders, such as lysosomal storage diseases.
Benefits
Benefits of whole genome sequencing include:
- Tens of thousands of genes are analyzed at once, so we can quickly detect almost any genetic issue.
- Results can be used to determine the best course of care during pregnancy, at delivery and after birth.
- If you plan to have more children, the results can help us estimate the chances of the same condition occurring again and enable more accurate prenatal diagnoses in future pregnancies.
Eligibility
Our Fetal Treatment Center offers rapid whole genome sequencing to pregnant patients if:
- An ultrasound shows a physical abnormality (or multiple abnormalities) in one or more of the fetus's major organ systems.
- You had or will have prenatal testing with amniocentesis or chorionic villus sampling (CVS). (If you don't have these tests during pregnancy, your baby may be able to have rapid whole genome sequencing after birth; see the criteria for newborns below.)
- At least one biological parent can provide a DNA sample (blood or saliva) to help with interpretation of the genome sequencing results.
We offer rapid whole genome sequencing for newborns in our NICUs for various reasons, including:
- The baby has physical features that suggest a genetic condition.
- Abnormal results on newborn tests suggest a genetic disease.
- The baby has unexplained seizures.
- The baby is seriously ill and the cause is unknown.
- There's a family history of genetic disorders.
- A prenatal ultrasound indicated a significant abnormality, but you didn't have amniocentesis or CVS before delivery.
As with fetal testing, at least one biological parent must provide a DNA sample (blood or saliva) for a newborn to have rapid whole genome sequencing.
Our locations (4)
Awards & recognition
-

Among the top hospitals in the nation
-

Top 10 in the nation for neonatology (UCSF Benioff Children's Hospitals)
-
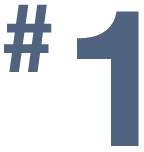
in number of fetal surgery clinical trials
-

successful open fetal surgery in the world





